iodine brain tissue staining
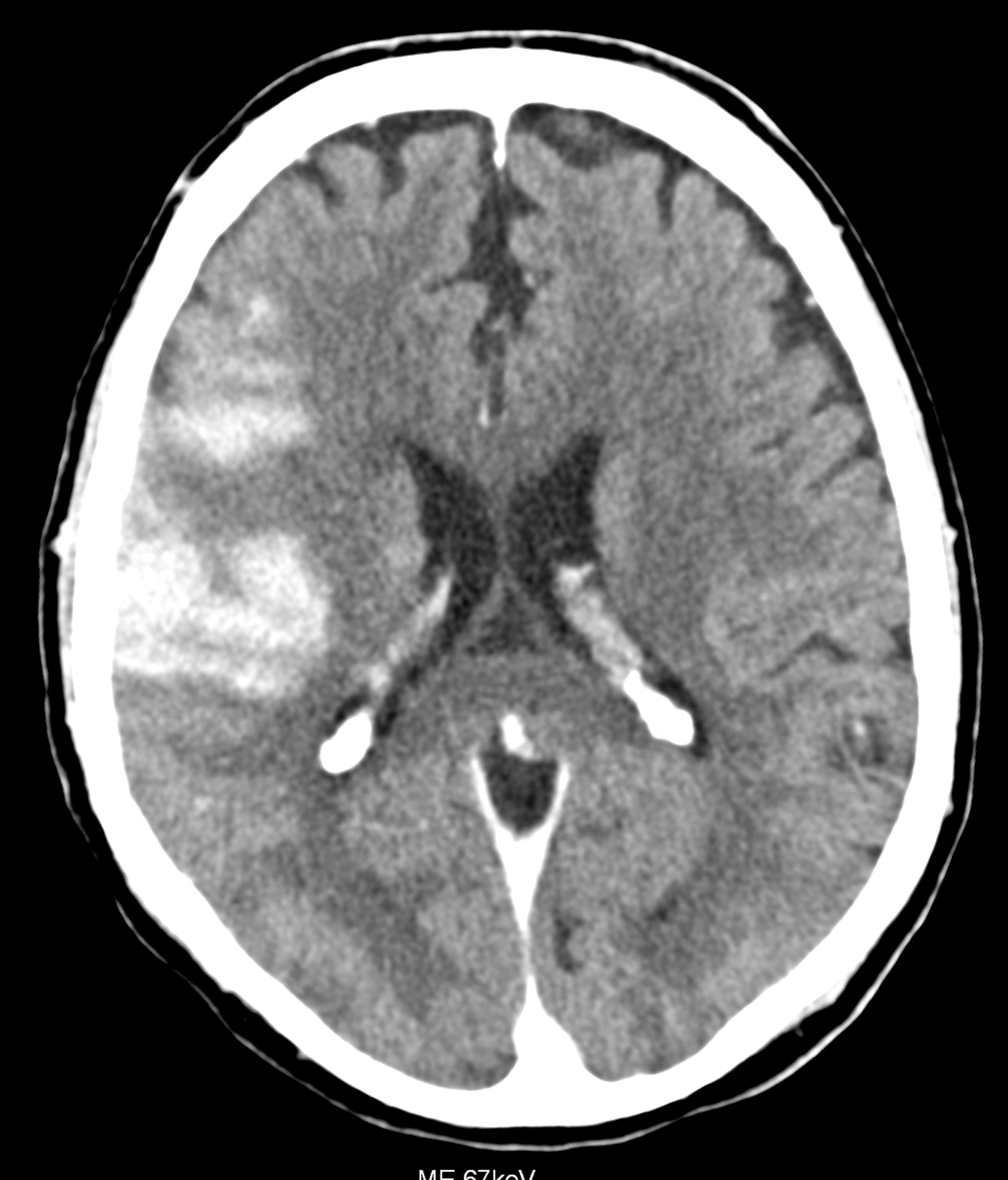
in the brain ischemia, multiple targeted iodine contrast agent injection are made into the affected territory during the mechanical thrombectomy. When the follow-up CT is made after the end-vascular intervention, the hyper-dense lesions may be caused by hemorrhage or the deposition of the iodinated contrast material – so-called staining. The bleeding into the ischemic tissue shows bad prognosis of the patient, the staining on the other side relatively better prognosis. The spectral analysis of photon-counting CT data enables the differentiation between iodine and blood. The territorial iodine staining was confirmed by the spectral analysis and then confirmed by the creation of the virtual non-contrast images. This technique is derived from the original method developed by the Pilsen and Forchheim authors in 2009
Ferda J, Novák M, Mírka H, Baxa J, Ferdová E, Bednárová A, Flohr T, Schmidt B, Klotz E, Kreuzberg B. The assessment of intracranial bleeding with virtual unenhanced imaging by means of dual-energy CT angiography. Eur Radiol. 2009 Oct;19(10):2518-22.
Naeotom Alpha Peak, University Hospital Pilsen, Czechia

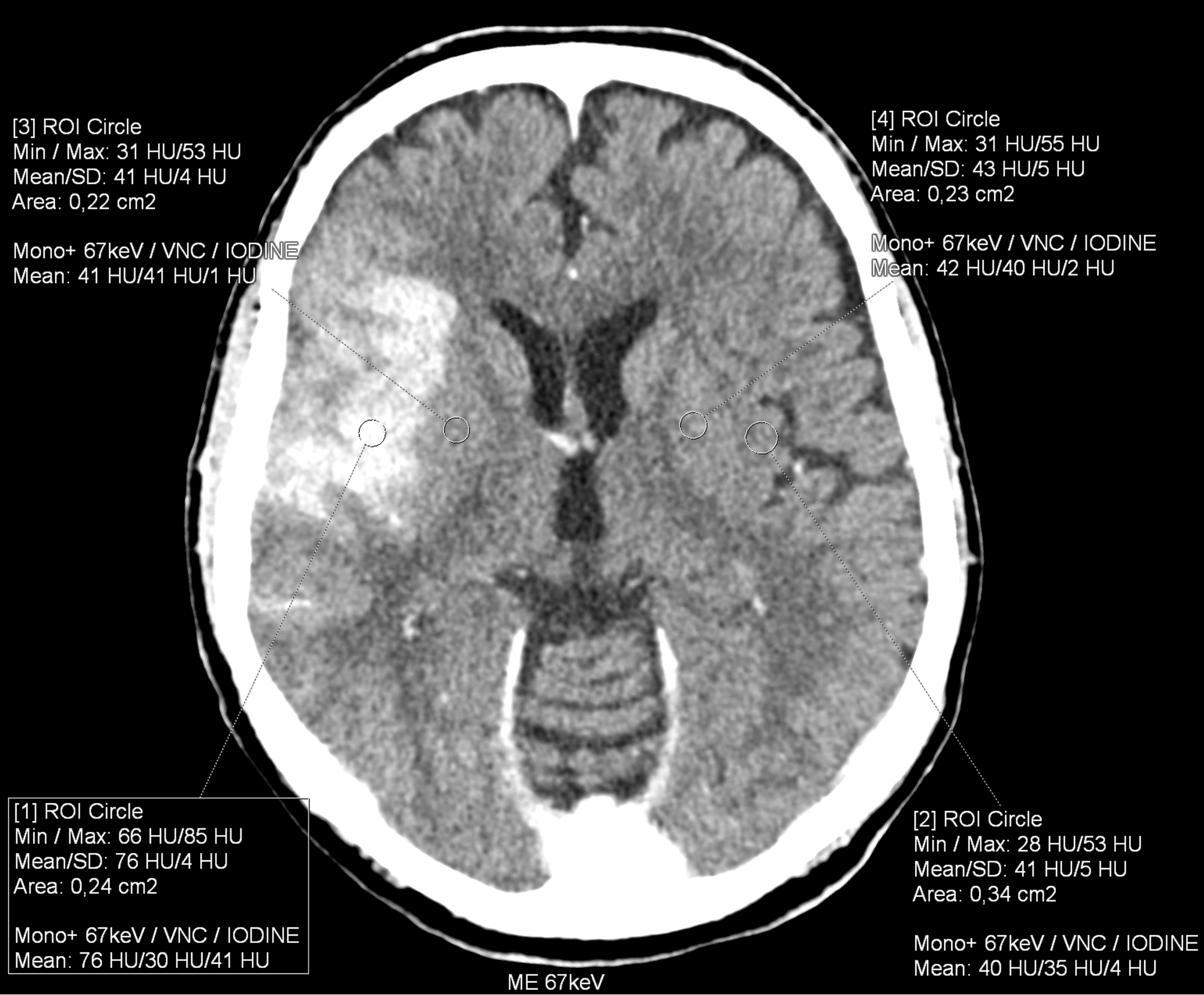
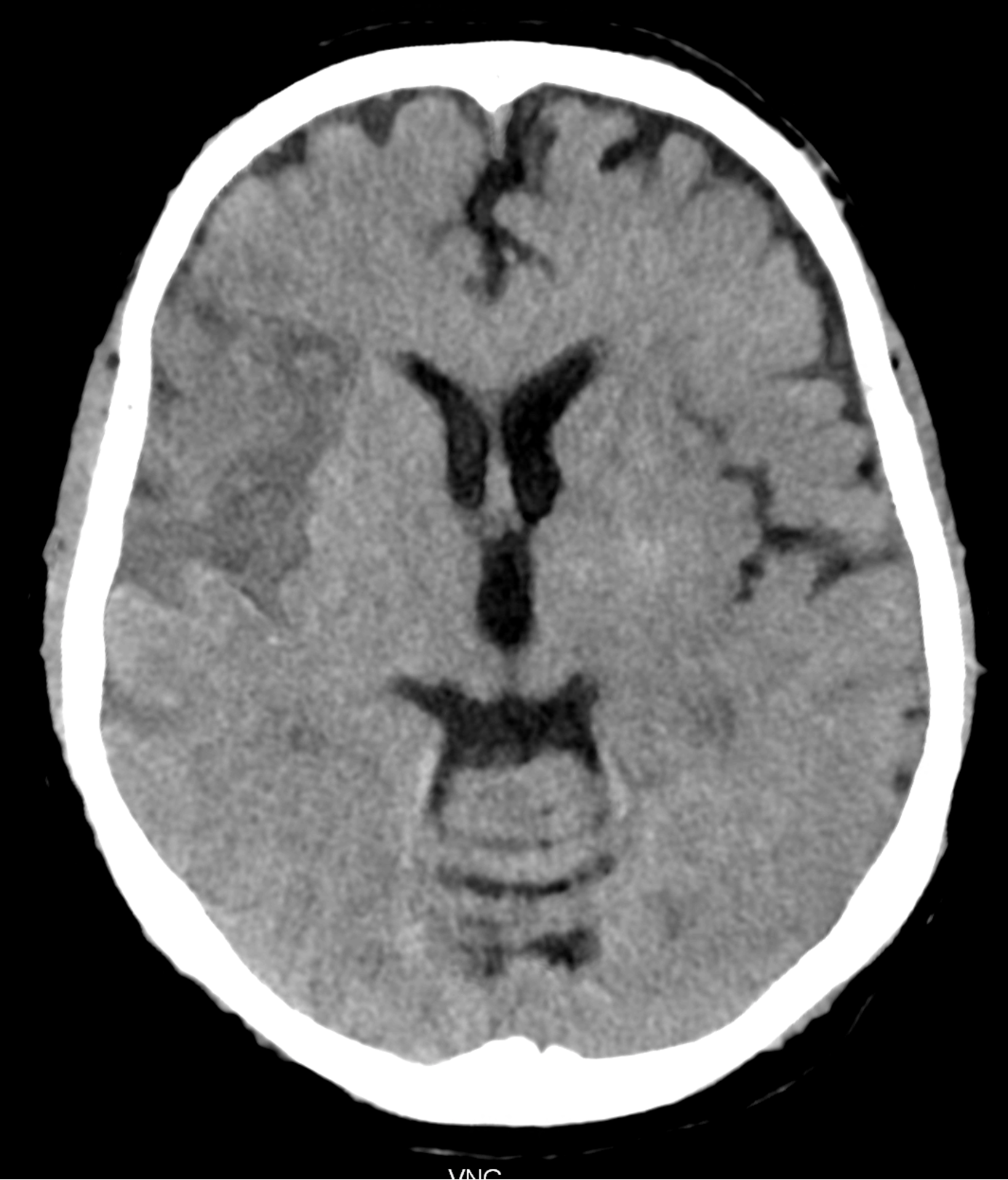
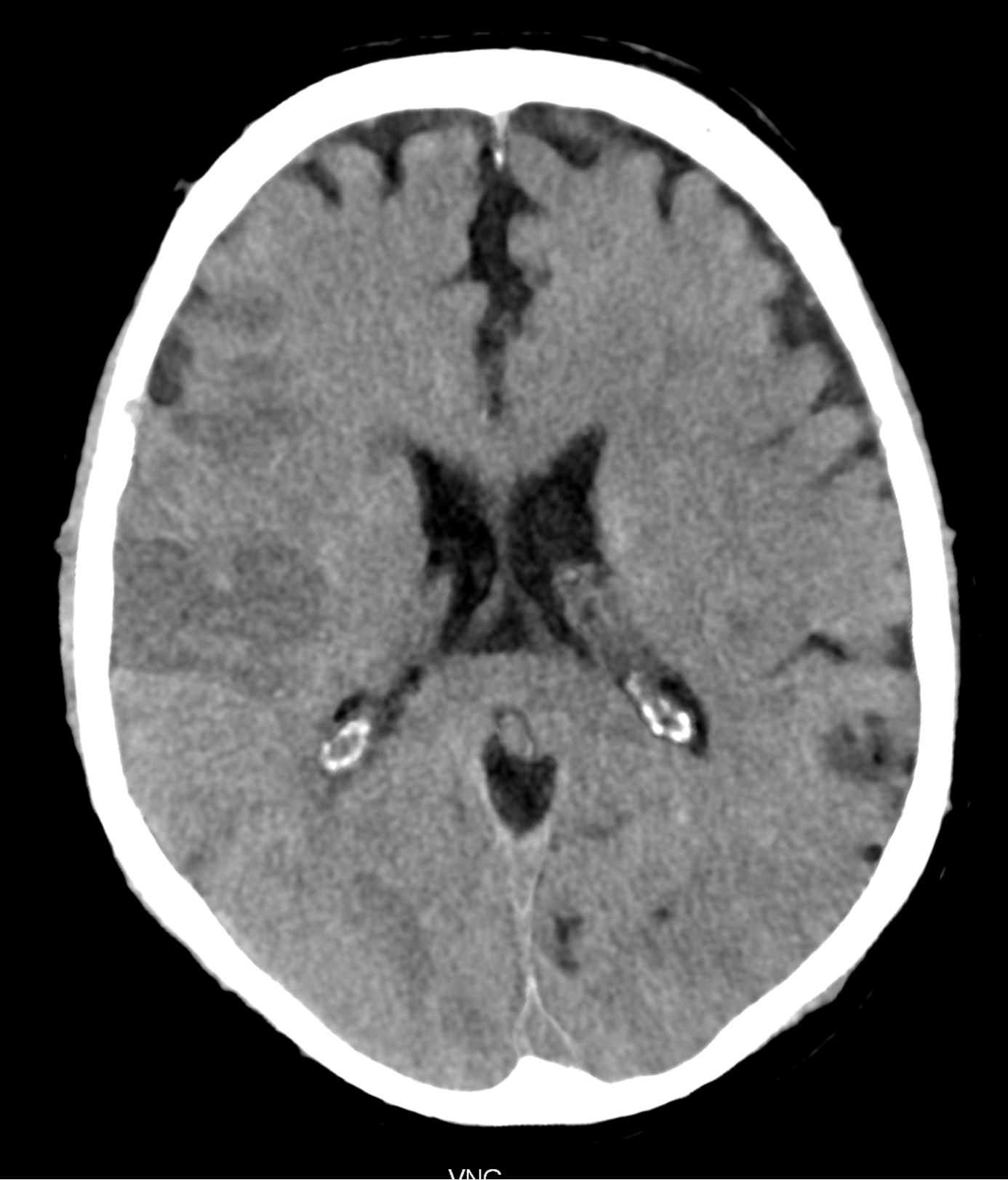
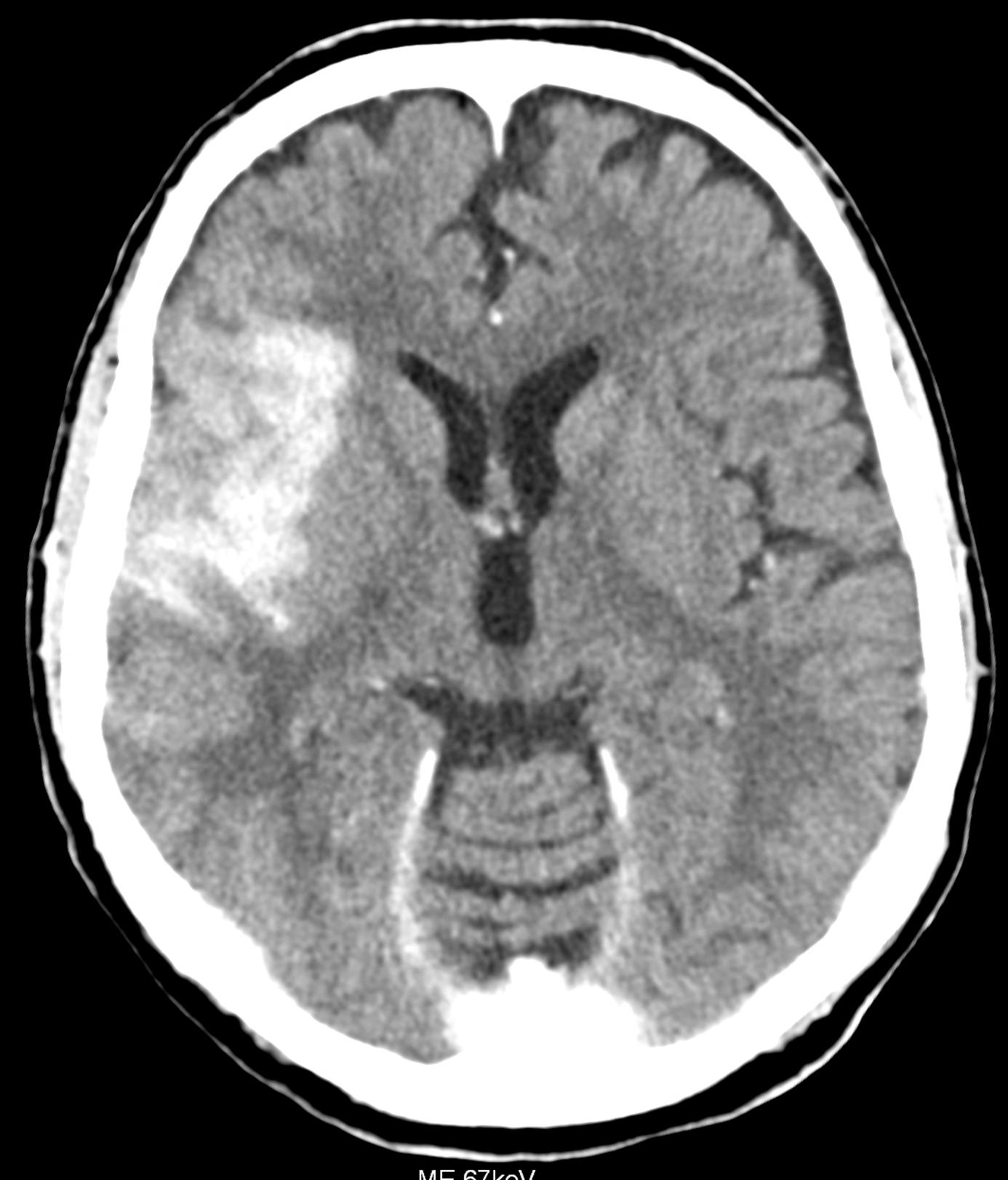
below in the upper row there are virtual non-contrast images derived from SPP of the brain PCCT, the lower row represents the images with the convention-like CT, with the ME of 67keV
Comments are closed.