Facial nerve peripheral paresis
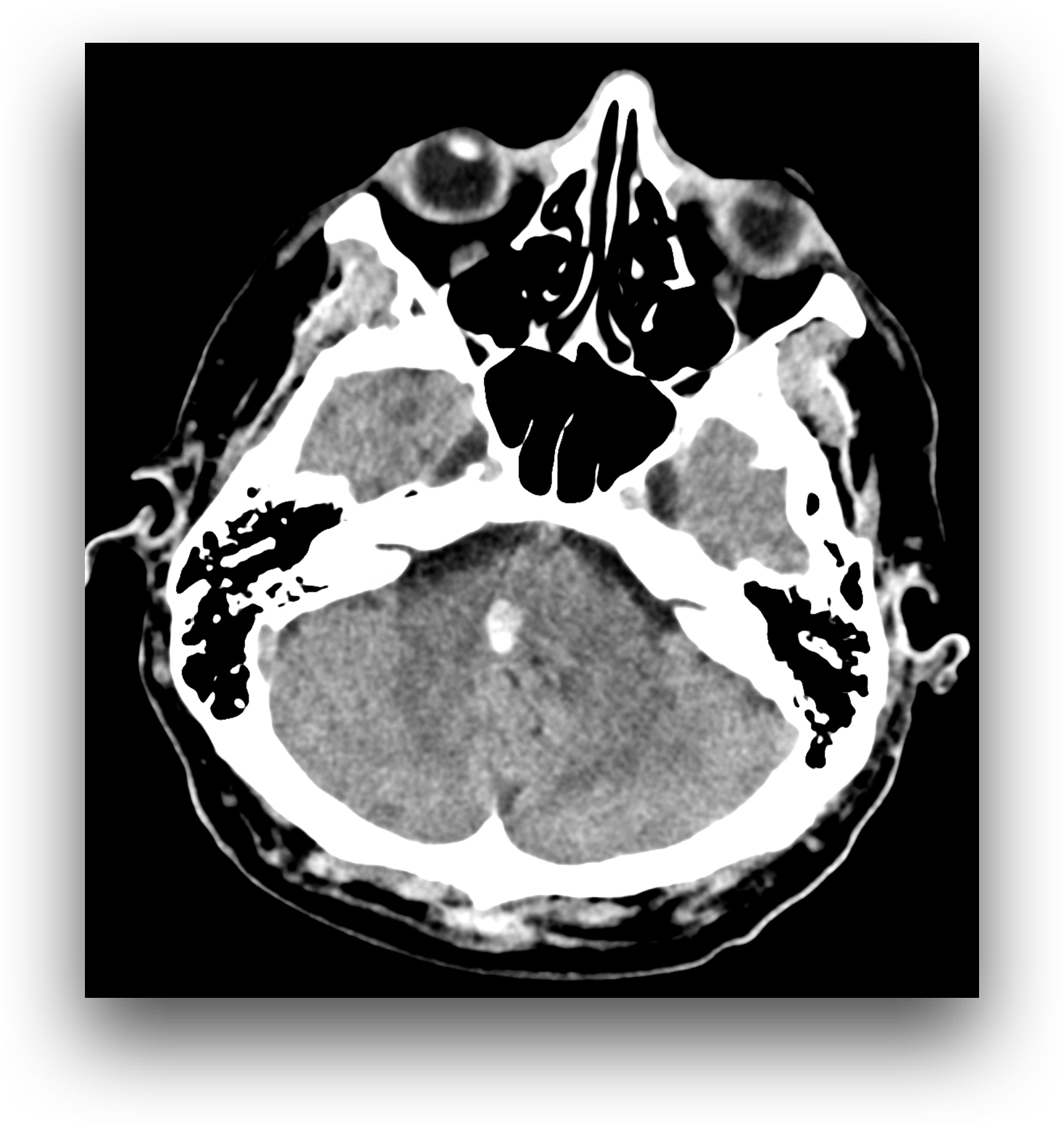
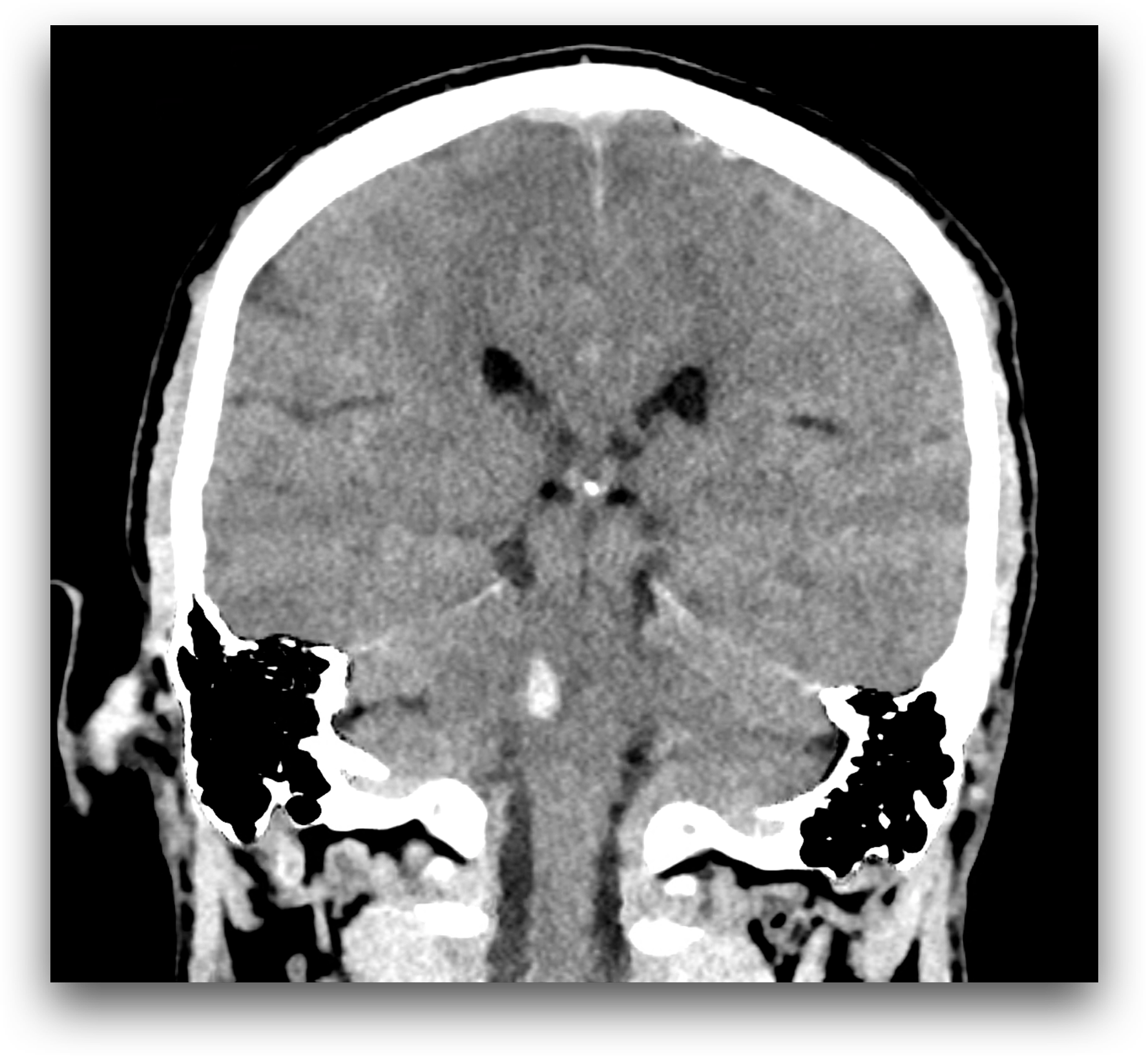
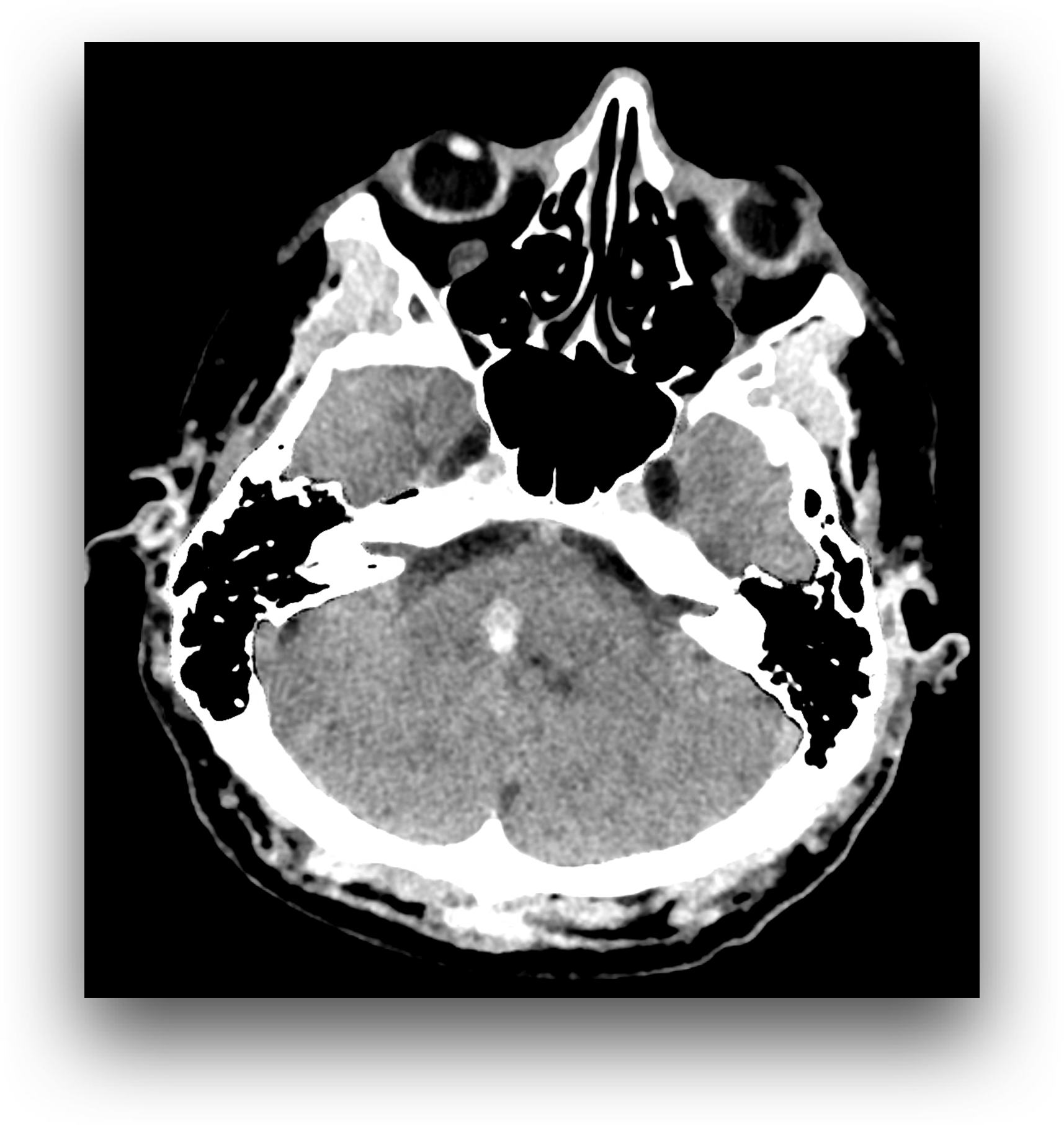
The examination was performed due to the symptoms of acute central stroke, clinically peripheral paresis of the right facial nerve and left-sided paresthesia. On CT scan, a haemorrhage is present in the right part of the transition between the pons and medulla oblongata, where the lesion is located in the region of the right nucleus of the facial nerve. Therefore, signs of peripheral paresis of the facial nerve are present. On the other hand, the presence of involvement in the area of the medulla oblongata above the level of the lemniscus medialis crossing indicates the involvement of ascending sensory pathways already in the place above their crossing at the level of the second neuron of the sensory pathway for tactile sensation. The use of virtual non contrast imaging suppresses the contrast of normal brain tissue at the expense of enhancing the signal of the hemorrhagic lesion. Supratentorial multiple vascular affection of the white matter of leukoaraiosis type, but also lacunar infarctions in the basal ganglia – at the region of head of the left caudate nucleus.
Naeatom Alpha Peak, University Hospital Pilsen, Czechia
Comments are closed.